BI-data Interface
Overview
It is a standard export functionality designed to enable the automated and scheduled export of production data from the RS Production system to external destinations for reporting and analytics. This data can be consumed by BI tools like Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, and Qlik to visualize trends, monitor performance, and support data-driven decisions.
Exports are configurable with flexible options for time intervals, date-time formats, time zones, destinations, and output formats. This supports seamless integration with cloud platforms, on-premise databases, and remote systems.
Destinations
This function offers several different types of destinations:
Destination | Supported Formats | Requires Edge Service |
|---|---|---|
Azure Blob Storage | CSV, JSON |
|
Local Folder | CSV, JSON |
|
SFTP Server | CSV, JSON |
|
SQL Server Database | Direct DB Export |
|
Azure SQL Database | Direct DB Export |
|
1. Azure Blob Storage
Ideal for those who want to access data from RS Production while developing applications on Azure.
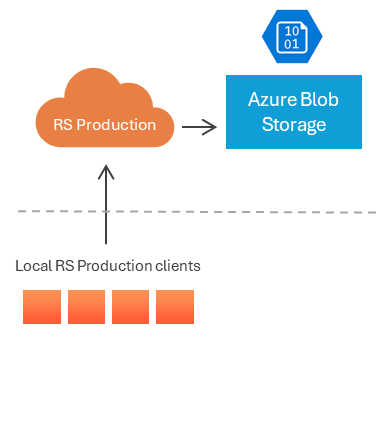
File Types Supported: CSV, JSON
SAS URL (Shared Access Signature):
Provides secure, time-bound access to Azure Blob containers.
Customer must:
Create a storage account in Azure.
Create a container with the name same as the installation number (6 digits).
Add an access policy specifying start and expiry time.
Generate and save the SAS URI for use in RS Production.
Supports archiving of historical data
2. Local Folder
Suitable for local development projects.
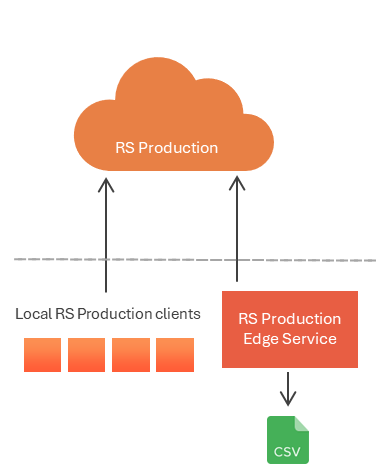
File Types Supported: CSV, JSON
Directory:
Specify a local directory path on the server hosting RS Production or Edge/OPC service
Supports archiving of historical data
Requires Edge service for cloud installations
3. SFTP Server
Suitable for those who develop locally.
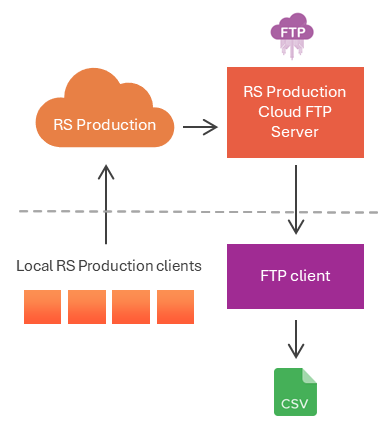
File Types Supported: CSV, JSON
Required details:
Server name (SFTP host)
Username
Password
Directory path to receive the exported files
Supports archiving of historical data
Requires Edge service installation for cloud installations using on-premise SFTP service
4. Azure SQL database
Ideal for those who want to use data from RS Production in applications developed on Azure.
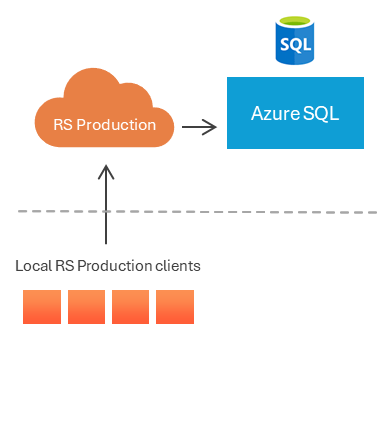
Required details:
Server name
Username
Password
Database name
This export option is compatible only for installations that process a single order or article at a time due to the primary key constraint enforced in the target schema.
5. SQL Server Database
Suitable for local development projects.
Required details:
Server name
Username
Password
Database name
Requires Edge service installation on on-premises SQL server database selection.
This export option is compatible only for installations that process a single order or article at a time due to the primary key constraint enforced in the target schema.
Setup Instructions
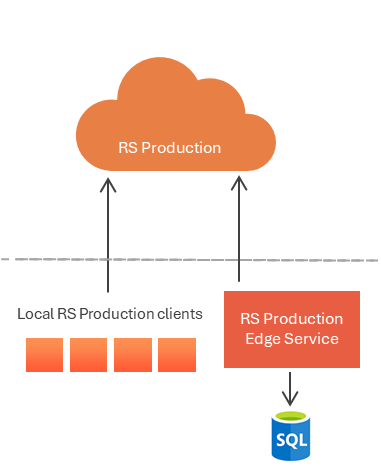
Edge service
Learn more about secure communication with the cloud Edge Service . Find details on how to Install Edge Service .
For SQL database (Azure / on-premise SQL server):
Before enabling this export, the following SQL script must be executed on the destination database server. This script creates the necessary schema structure to receive and store the exported data from RS Production.
Change the databasename from XXXXXX to your installation ID in RS
BI export database structure.sql
Settings
The Data export settings is available under Settings > Integration. Once enabled, the following parameters must be configured:
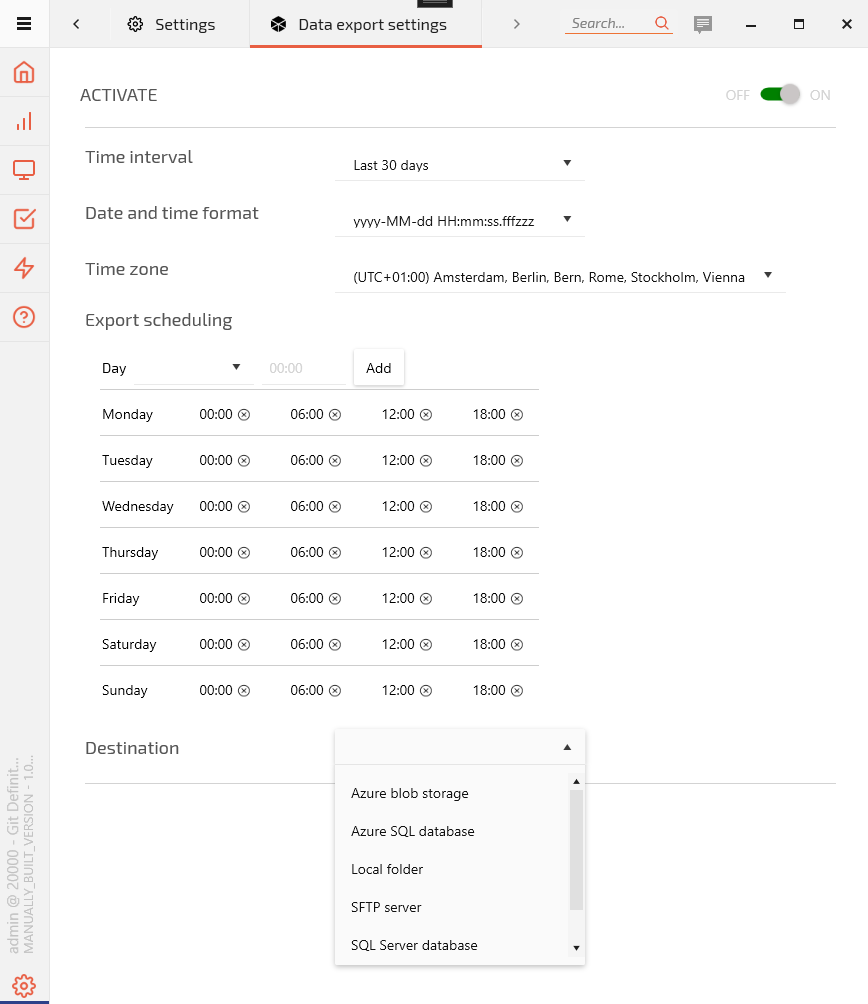
1. Time Interval
Select the desired time frame for regular exports:
Last 30 Days
Last 7 Days
From Yesterday
Today
2. Date and Time Format
Define the date-time format for exported data:
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff
MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ss.fff
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fffzzz
MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ss.fffzzz
3. Time Zone Selection
Specify the time zone to ensure timestamps in exported data match your organization’s time zone.
Default: (UTC+01:00) Amsterdam, Berlin, Bern, Rome, Stockholm, Vienna
4. Export Scheduling
Configure the frequency at which the export should run, x days at x time.
5. Destination
Choose one of the available destinations:
Azure Blob Storage
Azure SQL Database
SQL Server Database
SFTP Server
Local Folder
Default port used in the connection string is 1433 - if you need to change it, use comma in the formatting (e.g. 10.xx.xx.xx,1484)
Data Export Details
The system exports four categories of production data along with form data if the installation has an ACT license.
1. Settings
Defines OEE calculation logic for each installation:
Installation information
OEE calculation flags
CalculatePerformanceFromWeightedProducedUnits
MicrostopAsPerformanceLoss
ReworkAsQualityLoss
Fields | Comment |
|---|---|
InstallationID | Installation GUID |
Installation | Name of the installation |
CalculatePerformanceFromWeightedProducedUnits | Indicates if the produced amount on all the measure points are calculated equally regardless of what speed they are defined to run on. |
MicrostopAsPerformanceLoss | Indicates if the loss for microstops are moved from availability loss to speed loss |
ReworkAsQualityLoss | Indicates if the loss for rework are moved from speed loss to quality loss |
2. Stops
Captures detailed information about every stop event per shift at each measure point.
Installation and measure point details
Stop timing information (start, end, duration)
Reason and category of stop
Station and shift information
Operator comments
Fields | Comment |
|---|---|
InstallationID | Installation GUID |
Installation | Name of the installation |
MeasurePointID | Measure point GUID |
MeasurePoint | Name of the measure point/machine |
IntervalStart | Start time of a stop |
IntervalEnd | End time of a stop |
TotalStopDuration | Total stop time duration |
StopReason | If a stop is microstop, then it returns as ‘Micro stops’ If there is a stop on no worktime, then it returns as ‘No active order’ If there is no schedule on a machine, then it returns as ‘No schedule’ If a stop is not categorized, then it returns as ‘Uncategorized’ If a stop is categorized, then it returns the stop reason code. |
Categories | Interrupt reason categories |
Station | Name of the station on which the stop occurred |
Comment | Comments provided by operator user |
ShiftID | GUID of the shift instance when the stop occurred If a stop is of a longer duration, then ShiftID returns as an array of shift instance guids separated by comma(,). |
3. Stop Occasions
Provides summarized data about stop intervals across shifts for each measure point. It focuses on broader patterns and reliability metrics rather than individual events.
Installation and measure point details
Stop and productive occasion tracking
Metrics including:
Duration
Stop quantity
MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures)
MTTR (Mean Time To Repair)
Fields | Comment |
|---|---|
InstallationID | Installation GUID |
Installation | Name of the installation |
MeasurePointID | Measure point GUID |
MeasurePoint | Name of the measure point/machine |
IntervalStart | Start time of a stop |
IntervalEnd | End time of a stop |
Duration |
|
TotalStopDuration | Total stop time duration |
ScheduledDuration |
|
ProductiveDuration |
|
StopQuantity |
|
NumberOfProductiveOccasions |
|
MTBF | Mean Time Between Failures |
MTTR | Mean Time To Repair |
4. Worktimes
Logs the production activity per shift at each measure point, aggregated on an hourly basis.
Installation and measure point details
Shift information
Production order and article information
OEE metrics including:
Total, scheduled and excluded duration
Time breakdown (productive, downtime)
Unit production metrics
Fields | Comment |
|---|---|
InstallationID | Installation GUID |
Installation | Name of the installation |
MeasurePointID | Measure point GUID |
MeasurePoint | Name of the measure point/machine |
IntervalStart | Start time of the worktime |
IntervalEnd | End time of the worktime |
ShiftID | GUID of the shift instance |
Shift | Name of the shift |
ProductionOrder | Order number |
Article | Article number |
ArticleName | Article name |
ArticleType | Article type |
TotalDuration | The total duration(in seconds) |
ScheduledDuration | Time scheduled on the measure point |
ExcludedDuration | Time on which the stops were marked as excluded |
StopDuration | The total time when the measure point is stopped |
SetupStopDuration | The total time of changeovers |
NoWorkTimeStopDuration |
|
MicroStopDuration | The total time of all microstops combined |
ProductionTimeDuration | The total time when the measure point is producing |
UsedEffectiveTime |
|
ReworkedEffectiveTime |
|
ScrappedEffectiveTime |
|
OptimalProducedUnitsNoMicroStop |
|
OptimalProducedUnits | Amount of optimal produced units on time when machine was available |
ProducedUnits | Amount of produced units |
ApprovedUnits | Amount of approved units |
ScrappedUnits | Amount of scrapped units |
ReworkedUnits | Amount of reworked units |
5. Forms
Details on submitted dynamic forms. The system exports this data only with an ACT license.
If exported in file format, a file is generated for each form, structured similarly to the Filled forms table report in Office tools.
If exported to a database, the information is loaded into two form tables.
a. FormInstance
Stores metadata for each form submission.
Fields | Comment |
|---|---|
InstallationID | Installation GUID |
Installation | Name of the installation |
FormInstanceID | Form instance GUID |
FormID | Form GUID |
FormName | Name of the form |
FormVersion | Version of the form |
MeasurePointID | Measure point GUID |
MeasurePoint | Name of the measure point/machine |
Created | Datetime when the form was created |
Updated | Datetime when the form was last updated |
b. FormValue
Stores individual fields from the form submission as key-value pairs.
Fields | Comment |
|---|---|
InstallationID | Installation GUID |
FormInstanceID | Form instance GUID |
FieldID | Field GUID |
FieldName | Name of the field |
FieldValue | Value stored in the field |
OEE calculation
Availability
((ScheduledDuration - StopDuration - SetupStopDuration - NoWorkTimeStopDuration + (Setting.MicrostopAsPerformanceLoss ? MicroStopDuration : 0)) /
(ScheduledDuration - ExcludedDuration)) * 100Performance
It includes four distinct calculations based on the settings specified in the “Setting” table:
If both the MicrostopAsPerformanceLoss & CalculatePerformanceFromWeightedProducedUnits settings are enabled:
C#ProductionTimeDuration + MicroStopDuration > 0 ? ((UsedEffectiveTime - (Setting.ReworkAsQualityLoss ? 0 : ReworkedEffectiveTime))/ (ProductionTimeDuration + MicroStopDuration)) * 100 : 100If only the MicrostopAsPerformanceLoss setting is enabled:
C#OptimalProducedUnitsNoMicroStop > 0 ? (OptimalProducedUnitsNoMicroStop > ProducedUnits ? ((ProducedUnits - (Setting.ReworkAsQualityLoss ? 0 : ReworkedUnits)) / OptimalProducedUnitsNoMicroStop) * 100 : 100) : 100If only the CalculatePerformanceFromWeightedProducedUnits setting is enabled:
C#ProductionTimeDuration > 0 ? ((UsedEffectiveTime - (ReworkAsQualityLoss ? 0 : ReworkedEffectiveTime)) / ProductionTimeDuration) * 100 : 100If neither of the settings is enabled:
C#OptimalProducedUnits > 0 ? (OptimalProducedUnits > ProducedUnits ? ((ProducedUnits - (Setting.ReworkAsQualityLoss ? 0 : ReworkedUnits)) / OptimalProducedUnits) * 100 : 100) : 100
Quality
There are two different calculation methods based on the settings defined in the “Setting” table:
If the CalculatePerformanceFromWeightedProducedUnits setting is enabled:
C#UsedEffectiveTime - ScrappedEffectiveTime - (Setting.ReworkAsQualityLoss ? ReworkedEffectiveTime : 0) >= 0 ? (UsedEffectiveTime > 0 ? ((UsedEffectiveTime - ScrappedEffectiveTime - (Setting.ReworkAsQualityLoss ? ReworkedEffectiveTime : 0)) / UsedEffectiveTime) * 100 : 100) : 0If no settings are enabled:
C#ProducedUnits - ScrappedUnits - (Setting.ReworkAsQualityLoss ? ReworkedUnits : 0) >= 0 ? (ProducedUnits > 0 ? ((ProducedUnits - ScrappedUnits - (Setting.ReworkAsQualityLoss ? ReworkedUnits : 0)) / ProducedUnits) * 100 : 100) : 0
OEE
((Availability/ 100) * (Performance/ 100) * (Quality/ 100)) * 100